Install Boost C++ Libraries for a Specific User on Linux

Boost provides free peer-reviewed portable C++ source libraries. Libraries are intended to work well with the C++ Standard Library. Boost libraries are intended to be widely useful, and usable across a broad spectrum of applications. The Boost license encourages both commercial and non-commercial use.
Reference: https://www.boost.org/
Prerequisite
- GCC installed
Installation
Check the last archive of Boost C++ libraries available from: https://www.boost.org/users/download/
Download it on your machine.
cd ~/Downloads
wget https://dl.bintray.com/boostorg/release/1.70.0/source/boost_1_70_0.tar.bz2
tar jxf boost_1_70_0.tar.bz2
Some tar options are:
x- extractv- verbose output (lists all files as they are extracted)j- deal with bzipped filef- read from a file, rather than a tape device
Build Boost
cd ./boost_1_70_0
mkdir ~/.local/boost-libs
./bootstrap.sh --prefix=$HOME/.local/boost-libs
./b2 install
Make Boost available for your environment:
vi ~/.bashrc
Add at the end of ~/.bashrc:
export CPLUS_INCLUDE_PATH=$CPLUS_INCLUDE_PATH:~/.local/boost-libs/include
export LIBRARY_PATH=$LIBRARY_PATH:~/.local/boost-libs/lib
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:~/.local/boost-libs/lib
LD_LIBRARY_PATH is used by your program to search directories containing shared libraries after it has been successfully compiled and linked.
LD_LIBRARY_PATH is for dynamically linked (.so) libraries.
LIBRARY_PATH is used by gcc before compilation to search directories containing static libraries that need to be linked to your program.
LIBRARY_PATH for static (.a) libraries.
Reload ~/.bashrc:
source ~/.bashrc
or you can also use the shorter version of the command:
. ~/.bashrc
Test it
Edit a script Hello.cpp to check if Boost has been properly installed
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/format.hpp>
using namespace std;
using namespace boost;
int main()
{
unsigned int arr[5] = { 0x05, 0x04, 0xAA, 0x0F, 0x0D };
cout << format("%02X-%02X-%02X-%02X-%02X")
% arr[0]
% arr[1]
% arr[2]
% arr[3]
% arr[4]
<< endl;
}
Compile and run this script
g++ --std=c++14 Hello.cpp -o run
./run
Should return
05-04-AA-0F-0D
See also
date_range 02/09/2020
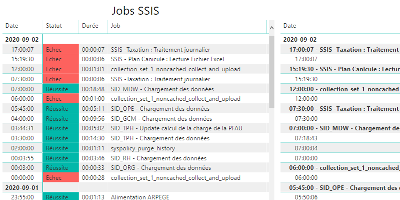
How to monitor SSIS job and package executions.
date_range 15/08/2020
Enable a network connectivity between Docker containers on CentOS 8.
date_range 07/04/2020
Sphinx and GitHub provide an efficient and free way to publish your documentation online. Here we describe how to do so.